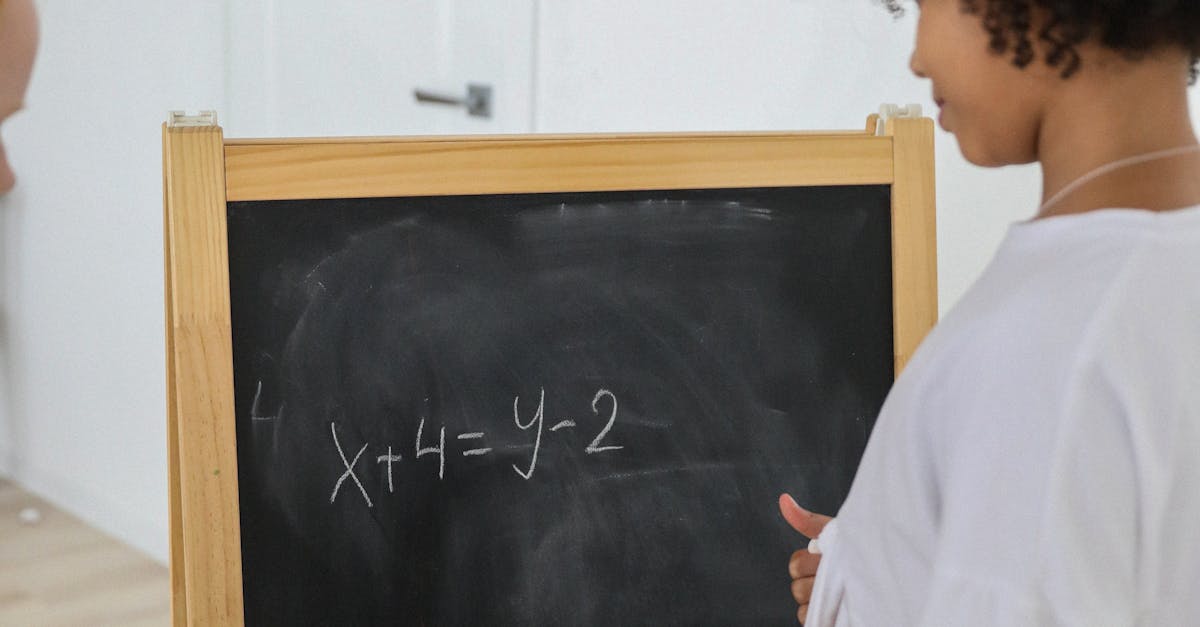
How to calculate equilibrium constant without concentrations?
You can work with the activity instead of the concentration when calculating the equilibrium constant. The activity is a measure of how much a particular chemical species is present in a solution, given the amount by which it dissolves. The activity of a species is directly related to its concentration. So, it makes sense to work with activity rather than concentration whenever possible.
How to calculate equilibrium constant without concentrations in aqueous solution?
We can use different approaches to solve this problem. The first method is to use the law of partial equilibrium and the principle of constant sum of the activities, which gives the ratio of the thermodynamic activities of the products and reactants at equilibrium. The Gibbs free energy equivalent of the reaction is used to compare the chemical potentials of the products and reactants. Then, the ratio of the reaction products’ Gibbs free energy and the Gibbs free energy of the reactants at a given temperature and pressure
Calculate equilibrium constant without concentrations?
To calculate the equilibrium constant, you need two states of an enzyme-substrate complex (ES) and two states of an enzyme with no substrate bound (E). The concentration of each species is given by the fraction of total enzyme in each state. To determine the ratio of ES to E, you need to know the amount of each species.
How to calculate equilibrium constant in aqueous solution?
Firstly, you need to calculate the concentration of the product (or reactant) in each compartment for a reaction. This will involve calculating the number of products (or reactants) based on the volume of the compartment. Then, you need to calculate the activity of each species (like the concentration of a chemical in solution multiplied by the activity coefficient), using the activities of the individual species and their respective activities coefficient values in that compartment. Finally, the equilibrium constant can be calculated as the ratio of the
How to calculate the equilibrium constant of a reaction without concentrations?
The most straightforward method for solving the equation for the equilibrium constant of a reaction is to use the law of mass action. The law of mass action states that the reaction rate is the product of the activity of each species involved in the reaction. If the activity of each species is equal to its concentration, then the reaction rate will equal the product of the concentrations of each species involved in the reaction and the reaction equilibrium constant will equal the ratio of the actual reaction rate to the rate of reaction if there is