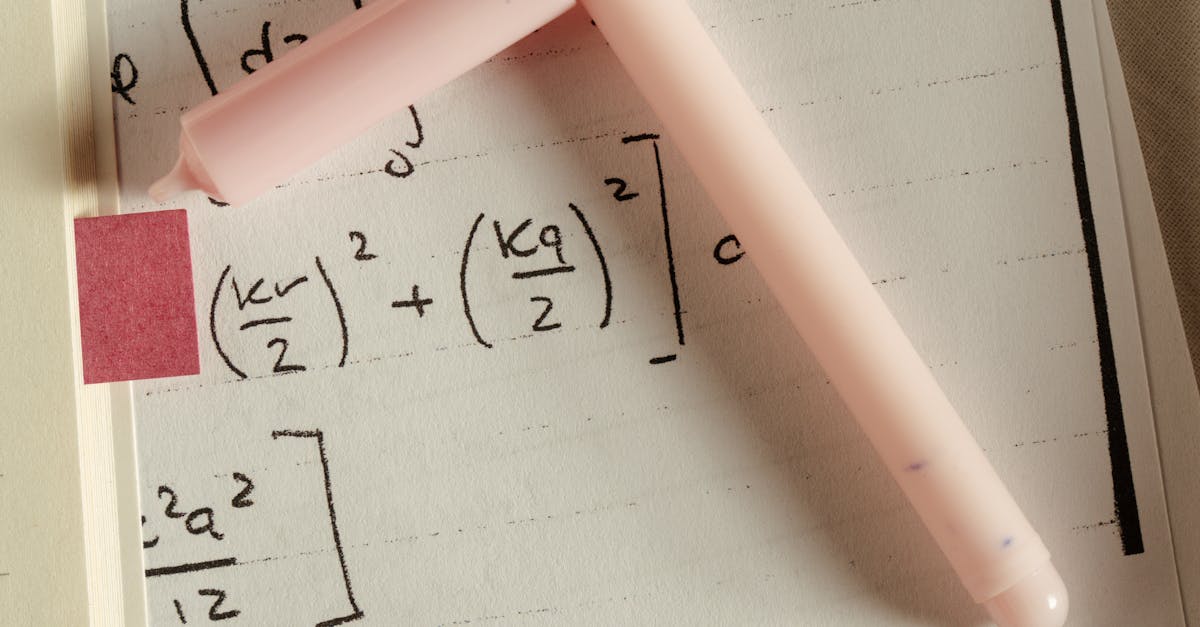
How to calculate the area of a parallelogram formula?
To determine the area of a parallelogram you need to know the length of each of the sides, as well as the two diagonals. If you don’t know the length of two sides, then take the average length of the two sides. Once you have the sides, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the area of a parallelogram with the known sides.
How to calculate the area of
If you are given two sides of a parallelogram you can use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the area of the parallelogram. You will need to know the length of each of the sides and the length of the hypotenuse. The Pythagorean Theorem states that a right triangle’s area is equal to the square of the length of its hypotenuse. The length of the hypotenuse is the length of a line drawn from each vertex of the
How to calculate the area of a parallelogram with parallel sides?
Given a parallelogram with parallel sides, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the area of a parallelogram with parallel sides. The Pythagorean Theorem states that the area of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. If you know the length of the two sides that form the base of a right triangle and you know the length of the other two sides that are opposite those two sides, you will be able to find the
How to calculate the area of a parallelogram with opposite sides?
The area of a parallelogram is equal to ||base||*||height||. The base is the length of one of the sides and the height is the length of the other. The easiest way to find the area of a parallelogram with opposite sides is to find the area of the base and subtract the area of the two triangles formed by the two sides.
How to calculate the area of a parallelogram with right angle sides?
To calculate the area of a parallelogram with right angle sides, you need to use the Pythagorean Theorem. It states that the sum of the squares of the legs of a right triangle equals the square of the hypotenuse. To use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the area of a parallelogram with right angle sides, you need the legs of the right triangle. The legs measure the sides of the parallelogram.