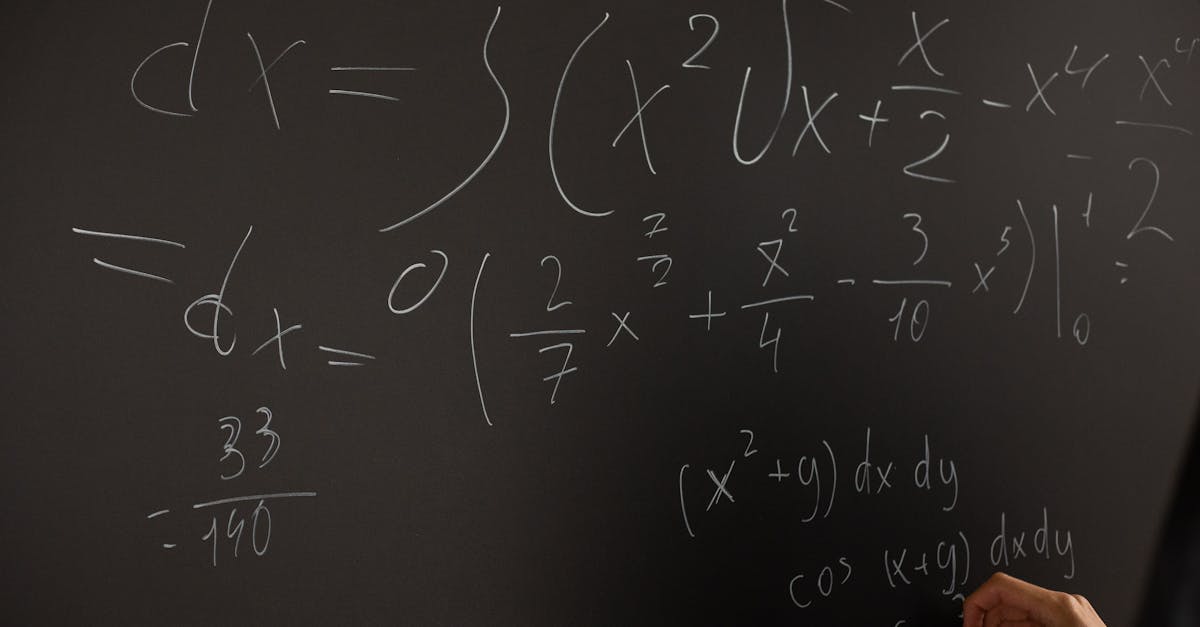
What does dissipate meaning physics?
Our search for meaning is as old as humankind. We try to understand what the meaning of life is, of people, of nature, of death itself. When we try to find meaning, we use the five senses along with the part of the brain called the neocortex, which deals with higher cognition. This includes what we hear, see, smell, taste, and feel.
What does dissipated mean physics?
In physics, energy can be transferred from one place to another in many ways. Energy can be the kinetic energy of particles or it can be stored in the potential energy of forces. When energy is transferred from one location to another, it can be either absorbed or dissipated. If the energy is absorbed, the energy is transferred to the location at which the energy is absorbed. If the energy is simply dispelled, it loses its energy to the location from which it was dispelled.
What does dissipate mean physics?
The word “dissipate”, when used in regards to energy, means to transfer energy from one place to another. Energy can be conserved or it can be transferred. If energy is conserved, then it will still be present in the form that it originally was. If energy is transferred, then it will no longer be present in the form it was before the transfer.
What does dissipate mean in physics?
Energy is known to be in a state of perpetual motion, with no beginning or end. This energy can be in different forms, such as motion, heat, light, electricity, magnetism, and chemical bonds. Energy is ‘dissipated’ when it loses its form and becomes ineffective. The concept of energy as an object of analysis is a concept that dates back to the ancient Greeks, though its physical nature was not discovered until the 17th century.
What does disappear in physics mean?
In physics, when a particle or energy (such as light or heat) vanishes, it either vanishes completely or vanishes to an infinitely small point. The vanishing of energy can be further described as the absorption of energy. The opposite of absorption is known as emission. Energy that is emitted does not simply disappear; rather, it becomes less dense than the surrounding area.